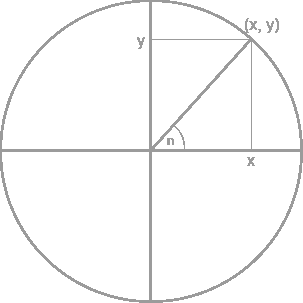
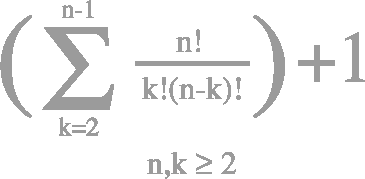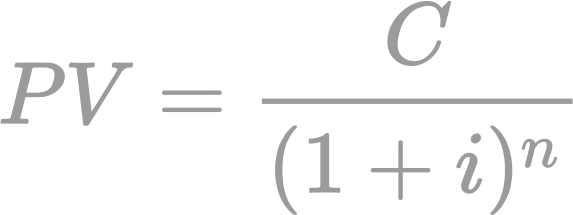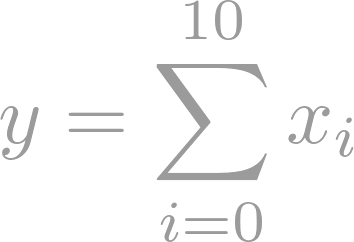Basic probability theory: laws of probability, conditional probability, independence, Bayes formula, random variables, discrete and continuous distributions, expectations, moments, moment generating functions, functions of random variables.
Special distributions: binomial, geometric, negative binomial, Poisson, hypergeometric, uniform, exponential, gamma, normal, laws of large numbers, the Central Limit Theorem.